|
| 表面能計算原理說明 |
|
表面能為固體與氣體間之界面張力的一般定義,如同液體的表面張力為液體與氣體間之界面張力以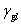 表示,同樣的固-氣間的界面張力以 表示,同樣的固-氣間的界面張力以 表示,然而表面能雖然可明確被定義,然而卻無法如液體一樣被直接測量. 表示,然而表面能雖然可明確被定義,然而卻無法如液體一樣被直接測量.
由楊氏熱力平衡方程式如下:
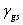 = = 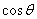 + +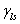
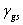 :固體表面能, :固體表面能,
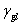 :液體表面張力, :液體表面張力,
 :固-液間界面張力, :固-液間界面張力,
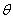 :接觸角 :接觸角
上述方程式右邊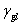 及 及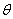 可由儀器測量而得,然而尚有兩個未知數,因此無法直接算出表面能 可由儀器測量而得,然而尚有兩個未知數,因此無法直接算出表面能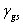 ,因此表面能並無所謂正確或標準值,只能由一些模型中提供另一組方程式以便求出
,這些模型皆有假設條件,因此所算出的結果只能算是表面能近似值. ,因此表面能並無所謂正確或標準值,只能由一些模型中提供另一組方程式以便求出
,這些模型皆有假設條件,因此所算出的結果只能算是表面能近似值.
目前常用的模型如下:
- Zisman Plot (critical
wetting tension)
- Fowkes
- Owens-Wendt-Rabel-Kaelble
(OWRK)
- Extended Fowkes
- Wu harmonic mean
- Equation-of-state
- Lewis acid/base
theory
使用上述方法各別計算,可能得到之結果彼此有高達25%的差異,然而每種方法皆有其適用的表面固體,然而卻無所謂正確或標準值,雖然如此,表面能仍具有原理的基礎性,可如液體表面張力般具備客觀性,同時對於一般所適用的模式,其誤差還是在可接受的範圍內.
臨界表面張力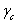 -
Zisman
Plot -
Zisman
Plot
由楊氏熱力平衡方程式如下:
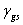 = =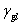  + +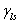
其中:
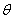 :接觸角, :接觸角,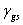 :固體表面能, :固體表面能,
 :液體表面張力, :液體表面張力,
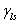 :固-液間界面張力 :固-液間界面張力
適用: 表面能<
100 mN/m(低能表面)的固體表面,液滴在表面形成的接觸角主要是液體表面張力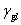 的函數,對於給定的固體表面和同系列的相關液體(如烷?
二烷基脂和烷基鹵化物), 的函數,對於給定的固體表面和同系列的相關液體(如烷?
二烷基脂和烷基鹵化物),  與 與 有近似線性關係.對於非極性液體,關係十分相符,然對於高表面張力的極性液體,關係並不十分符合,直線開始彎曲. 有近似線性關係.對於非極性液體,關係十分相符,然對於高表面張力的極性液體,關係並不十分符合,直線開始彎曲.
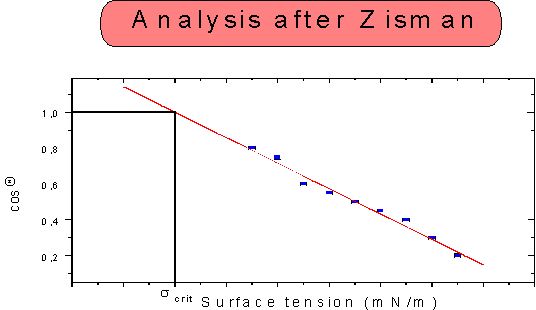
從 對 對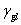 的曲線中,在 的曲線中,在 =1時,可以得到固體的表面張力,稱為潤濕臨界表面張力,它的定義是指液體剛好鋪展到固體表面產生完全潤濕時的表面張力,即 =1時,可以得到固體的表面張力,稱為潤濕臨界表面張力,它的定義是指液體剛好鋪展到固體表面產生完全潤濕時的表面張力,即 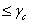 時,液體將鋪展,當 時,液體將鋪展,當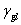  時,液體將形成液滴,具有非零接觸角. 時,液體將形成液滴,具有非零接觸角.
|
Fowkes方法
假定: 液體及固體表面張力可分為色散力和極性作用力,若固液兩相中有一相是非極性,則固液之間只有色散力相互作用,無極性作用力:
 ; 無極性作用力,則 Ip
= 0.
; 無極性作用力,則 Ip
= 0.
即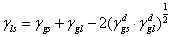
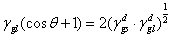 或
或 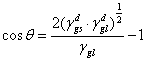
式中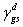 和 和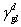 分別表示固體和液體表面張力的色散力部份. 分別表示固體和液體表面張力的色散力部份.
根據(1.4),  對 對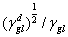 作圖得一直線,其斜率為 作圖得一直線,其斜率為 ,
從直線斜率可得到固體的 ,
從直線斜率可得到固體的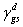 值. 值.
對於非極性固體, 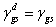 ,
故用Fowkes方法,可得到非極性固體的表面能. ,
故用Fowkes方法,可得到非極性固體的表面能.
對於非極性液體,也有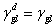 ,
根據(1-4)式, 可得出下式: ,
根據(1-4)式, 可得出下式:
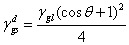
當 時,用Zisman方法得到的非極性固體臨界表面張力 時,用Zisman方法得到的非極性固體臨界表面張力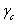 可表徵其固體的表面能. 可表徵其固體的表面能.
Owens-Wendt-Rabel-Kaelble
(OWRK) Method
假定:
分子色散力(disperse)和極性力(polar)為各自獨立作用且合力可加總
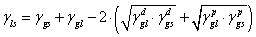
測試液體數量: n
>= 2
Extended
Fowkes Method
假定:
分子色散力(disperse),極性力(polar)及氫鍵力(hydrogen-bond)為各自獨立作用且合力可加總


測試液體數量: n
>= 3
Wu
(harmonic mean)方法
1. 使用倒數平均法計算不同分子間的作用力
2. 不僅考慮色散力,也同時考慮分子間極性作用力的影響.
得到下列公式:
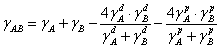
式中 表示表面張力的極性影響力, 表示表面張力的極性影響力,
 和 和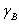 分別表式固體表面能和液體的表面張力,故只要測兩種或兩種以上極性不同的液體在固體表面的接觸角,解聯立方程式,即可得出固體表面能 分別表式固體表面能和液體的表面張力,故只要測兩種或兩種以上極性不同的液體在固體表面的接觸角,解聯立方程式,即可得出固體表面能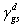 和 和 值. 值.
Equation-of-State
(Neumann)
假定: 固體,液體表面張力和固液界面張力間存在某種關係,且表面張力及界面張力並非各種作用力之加總結果
 [1]
[1]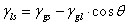 [2]
[2]- Young’s Eq.: In
combination with Eq.
[2], the following
equation-of-state
was derived :
 [3]
[3]- The value of
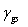 is
determined using the
Newton's routine from
Eq. [3]. is
determined using the
Newton's routine from
Eq. [3].
- 測試液體數量: n
= 1
Acid-Base
method
假定固體表面自由能藉由三大項所組成:非極性項(分散力項)、路義士酸(Lewis
acid)項、。路義士酸鹼對(Lewis
acid-base)交互作用,意指電子排斥者與電子接納者間的交互作用,前者大部分系統由於氫鍵所造成。(i.e.
Good and Girifalco equation)
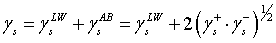 ………………………………
(1) ………………………………
(1)
其中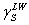 為非極性項,理夫緒茲-凡德瓦爾力(Lifshitz-van
der Waals), 為非極性項,理夫緒茲-凡德瓦爾力(Lifshitz-van
der Waals),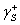 為電子接受者,而 為電子接受者,而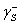 為電子排斥者間的作用力。 為電子排斥者間的作用力。
方程式(1)若為固體與液體間的表面自由能交互作用力則可表示成:
(i.e. van Oss et al.
approach)
 ………………………(2) ………………………(2)
然而,利用Young’s equation
:
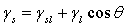 …………………………………………………………(3) …………………………………………………………(3)
和黏著濕潤之自由能按照Dupre’ equation
:
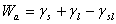 ……………………………………………………………(4) ……………………………………………………………(4)
將(2)式、(3)式和(4)式結合可得:
 ……………(5) ……………(5)
其中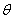 為接觸角,而 為接觸角,而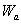 為液體在固體表面的黏著功。方程式(5)可以利用最少三種測試液體(表面張力各組成項為已知)來測量接觸角,而求得固體表面自由能。而利用已知的測試液體表面張力求方程式(5)中的固體表面自由能中的三大組成項(非極性項、路義士酸項和路義士鹼項)。解三個方程式(5)的同時,假設固體表面自由能的組成不會隨著使用不同測試液體測量而改變。另外,三種測試液中必須一者為非極性溶劑(可使用二碘甲烷),用以求非極性項( 為液體在固體表面的黏著功。方程式(5)可以利用最少三種測試液體(表面張力各組成項為已知)來測量接觸角,而求得固體表面自由能。而利用已知的測試液體表面張力求方程式(5)中的固體表面自由能中的三大組成項(非極性項、路義士酸項和路義士鹼項)。解三個方程式(5)的同時,假設固體表面自由能的組成不會隨著使用不同測試液體測量而改變。另外,三種測試液中必須一者為非極性溶劑(可使用二碘甲烷),用以求非極性項( );另一者為具有強極性溶劑(可使用乙二醇),另外再利用兼具極性與非極性的溶劑(可使用水),用以求極性項( );另一者為具有強極性溶劑(可使用乙二醇),另外再利用兼具極性與非極性的溶劑(可使用水),用以求極性項(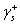 、 、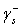 ),方能符合經驗式的計算。 ),方能符合經驗式的計算。
氫鍵為分子間作用力最常見的形式,會構成兩相間吸附與界面張力的自由能-鹼對,氫鍵能用Lewis酸-鹼理論完全描述,酸為電子接受者,鹼為電子提供者.
Van Oss and Good 研究非極性液體及氫鍵液體對固體潤濕行為.
若固液體皆為極性;則
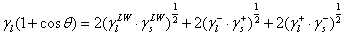
若固液體其中之一為極性;則 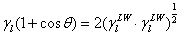
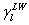 :
理夫緒茲-凡德瓦爾力(Lifshitz-van
der Waals) :
理夫緒茲-凡德瓦爾力(Lifshitz-van
der Waals)
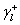 :
路義士酸(Lewis acid)項 :
路義士酸(Lewis acid)項
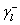 :
路義士鹼(Lewis base)項 :
路義士鹼(Lewis base)項
常用於表面能測量之液體須有足夠的表面張力,以避免完全鋪展於樣品表面,同時要有較高沸點及使用之安全性考量,故一般可選擇下列幾種液體:
Table
1典型測試液體 |
液體
|
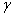 (表面張力) (表面張力)
|
 LW LW
|
 AB AB
|
 A A
|
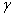 B B
|
Water
純水 |
72.8 |
21.8 |
51 |
25.5 |
25.5 |
Glycerol
甘油 |
64 |
34 |
30 |
3.92 |
57.4 |
Formamide
甲醯胺 |
58 |
39 |
19 |
2.28 |
39.6 |
Methylene
Iodide
二碘甲烷 (非極性) |
50.8 |
50.8 |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Ethylene
Glycol
乙二醇 |
48 |
29 |
19 |
1.92 |
47 |
註: 內部分子力可區分為兩大項,常用表示名稱如下:
- LW = Liftshitz-van
der Waals理夫緒茲-凡德瓦爾力
- London倫敦力
- non-polar非極性力
- dispersive forces
色散力
- AB = (Lewis) acid/base
(路易士)酸/鹼對
- polar forces極性力
表面能計算公式適用表:
Method |
Information |
Min.
no. of liquids |
Application |
Examples |
Zisman |
Critical
surface tension |
2 |
Non-polar
solids |
PE,
PTFE, waxes |
Fowkes |
Disperse
parts of surface
free energy |
2,
non-polar liquids |
Non-polar
system |
PE,
PTFE, waxes |
OWRK |
Disperse
and polar? parts
of surface free
energy |
2 |
universal |
Polymers,
aluminum, coating,
vanishes |
Extended
Fowkes |
Disperse,
polar and hydrogen
parts of surface
free energy |
3 |
Specific
questions of surface
properties |
Plasma,
or corona treated
polymers |
Wu
( Harmonik Mean
) |
Disperse
and polar? parts
of surface free
energy |
2,
at least one polar
liquid |
Low
energetic systems
|
Organic
solutions, polymers,
organic pigments |
Acid-Base
Theory |
Disperse,
acid and base
parts of surface
free energy |
3 |
Specific
questions of surface
properties |
Biological
system |
Equation
of State Theory |
surface
free energy |
1 |
universal |
Polymers,
aluminum, coating,
vanishes |
Work of Adhesion of
liquid to solid 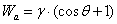
Work of Cohesion of
liquid to itself 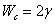
Spreading Coefficient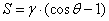
Wetting tension of liquid
to solid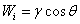
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|